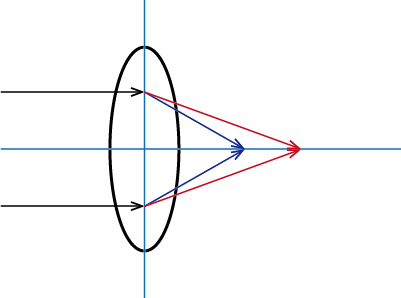
Aberration is the deviation from the ideal image formation in the optical system.
It is divided into two include: single chromatic aberration and monochromatic aberration.
You can further break down from here.
- Monochromatic aberration (axial chromatic aberration, magnification chromatic aberration)
- Single chromatic aberration (spherical aberration, coma aberration, astigmatism, field curvature, curvature aberration)
1. Monochromatic aberration
Chromatic aberration occurs due to the difference in refractive index depending on wavelength (color).
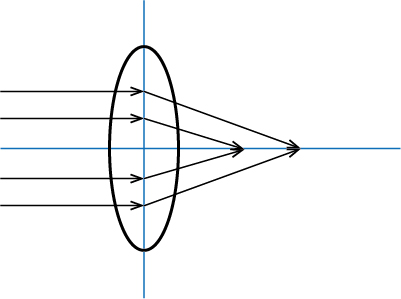
<About monochromatic aberration>
The focal point is connected at one point. However, the refractive index varies with the wavelength, the focal position will be shifted. This will occur as color drift and color blur on the screen.
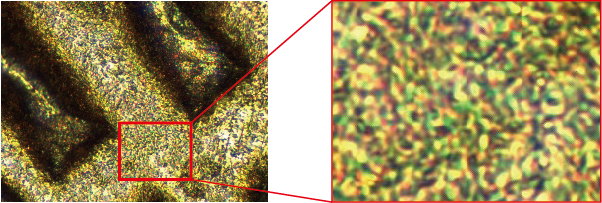
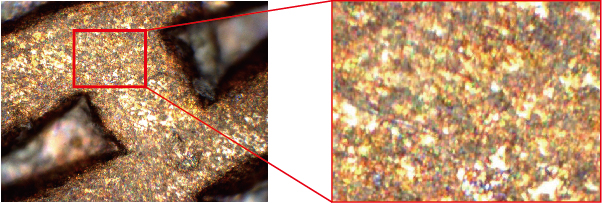
It is a photograph of 10 yen coin at 1000 times.
The above picture was taken with the ultrahigh magnification microscope (SH350PC-2R) with low price.
The picture below is taken with a super high magnification microscope (USH130CS-H1) using a high performance lens
| ●Taking by the ultra-high magnification microscope (SH350OC-2R) with low price | |
 |
|
| ●Taking by a ultrahigh magnification microscope (USH130CS-H1) using a high performance len | |
 |
|
You can see that color misalignment occurs when enlarging a part of the above picture (taken with the ultrahigh magnification microscope (SH350PC-2R)
2. Monochromatic Aberration
Monochromatic aberration, excluding curvature aberration, arises from variations in the angle of incident light passing through the lens and differences in the position of passage (inside and outside the lens), resulting in disparate refractive indices.
Symptoms such as contour blur and smudging manifest on the screen as a consequence.
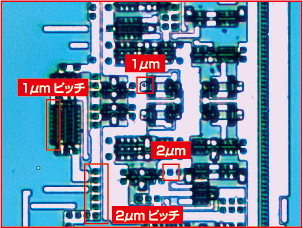
2. Actual footage of monochromatic aberration
This image was captured at 1000x magnification of the surface of a silicon wafer. The photograph on the left was taken using a high-magnification microscope, specifically the discontinued model SH350PC-2R. On the right, the image was captured using an ultra-high-magnification microscope equipped with a high-performance lens, the USH130CS-H1.
 |
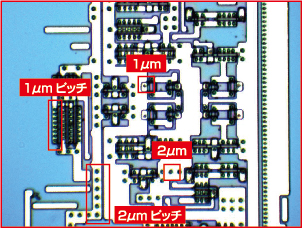 |
| Taking by the ultra-high magnification microscope (SH350PC-2R)with low price | Taking by a ultrahigh magnification microscope (USH130CS-H1) using a high performance lens |
The picture on the left shows a blurred outline.
(3) Spherical Aberration
* Spherical aberration does not cause blur.
It results in the symptom of curved lines around the edges of the screen. This symptom is divided into two types: pincushion and barrel distortion.
(For more information on spherical aberration, please refer to “What is Distortion?”)